The History and Future of Cellular Technology
The incredible pace of cellular technology evolution over the past decades has been near miraculous.
Coverage improved dramatically, data is vastly cheaper, and the wireless speeds possible with the latest devices rival landline broadband performance!
Best of all, this rapid pace of advancement shows no signs of slowing down. If anything, the tempo is only quickening as every carrier jockeys to take the lead in building next-generation 5G networks.
But just what on earth is 5G? Does it even matter how many Gs you have?!?
And what is 4G/LTE, for that matter - and what was it that came before?
Behind the scenes, the cellular world has an alphabet soup of technical standards and protocols designed to push more bits faster with each new generation.
The deeper technical details are more than most mortals should ever need to worry about.
But if you're interested in a high-level look into the evolution of cellular technologies and what to expect in the years ahead, this is the geek-level guide for you.
If you're a member, please log in above to see your exclusive content.
Don't need a membership? Other ways you can support our work here:
-
As seen in our videos!
-
Get a FREE Month of Starlink!
And our team will get one too!
-
Get a FREE Month of T-Mobile Unlimited Data
Join the Calyx Institute, and get a bonus month - and we do too!
-
Save $20 on Visible
Verizon's prepaid phone plan, we also get a $20 credit.
-
Leave a Tip!
Send our team some beer money!!
-
Share About Us!
Link to our content, tell others about MIRC. It's Free!
It is with huge gratitude to our members for making the free unbiased educational content on our site possible. We're not sponsored, you'll find no 3rd party ads and we don't sell gear or data plans.
Our members get exclusive access to our in-depth content, classrooms, vendor discounts (that can save you more than membership!), alerts, insider info and interactive guidance. They can even book private advising sessions.
If mobile internet is an important part of your lifestyle, consider helping make MIRC possible by joining or supporting our mission.
Where We Have Been
Cellular technology has (so far) gone through four major generations and is currently in the fifth generation. New cellular generations come along roughly once every decade, but they also expand, improve, and iterate over their lifecycles.
Here's a look back at the old days when things like basic text messaging seemed exotic and new.
What Is a G?
Long ago, the carriers adopted “G” for “Generation” as a simple marketing shorthand. When you see terms like 3G, 4G, and 5G, that’s all they mean—3rd generation, 4th generation, etc.
Devices of a given generation are usually compatible with at least one or two prior generations, an essential trait since the cellular network technology overlaps as carriers transition from one generation to another.
But the reverse is not true—a third-generation device will miss out entirely on all the speeds and technical advancements that have come with 4G technologies, and 4G/LTE technology devices cannot take advantage of the improvements of 5G networks. This is why upgrading your cellular devices regularly is beneficial so that you do not fall too far behind the technology curve.
Here’s a handy little infographic we created that will hopefully illustrate the evolution of cellular data technology standards a little better:
The changes between different generations of cellular technologies involve redefining the rules of how towers and devices communicate with each other, which allows new gear to be developed under those new specifications.
Think of it like the 1960s, when the maximum highway length for a vehicle was 35'. These days, the maximum length is 45', which results in larger vehicles transporting more commercial goods across the country, buses that move more people, and motorhomes with more luxuries.
In other words, evolving the standards to take advantage of newer technologies enables a new generation of more advanced devices that would have been impossible before.
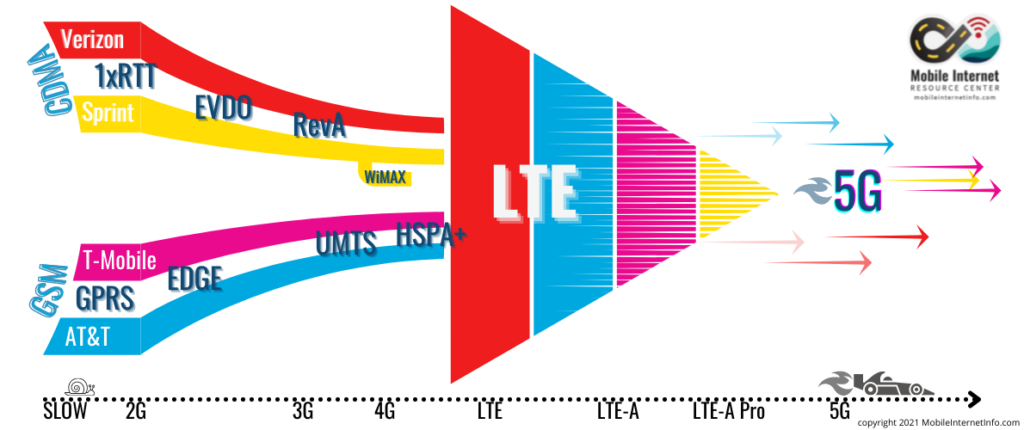
The Olden Days – 1G, 2G, 3G
There used to be two competing and fundamentally very different wireless technologies: CDMA and GSM.
Sprint and Verizon in the USA used CDMA, and most of the rest of the world used GSM.
As the graphic above shows, each of these two technologies had its own evolving and incompatible standards.
CDMA and GSM competed throughout the 3G era, but like many technological standards battles, there could be only one.
The 4G Revolution
Early on in the 4G era, Sprint bet big on a 4G technology called WiMAX and rushed to be the first to bring next-generation 4G service to market.
Meanwhile, Verizon predicted that the future would be the next generation of GSM technology known as LTE (aka Long-Term Evolution) and began aggressively building out the first and largest 4G/LTE network in the United States.
AT&T was also GSM-based but lagged behind Verizon in promoting and deploying LTE.
Seeing the LTE writing on the wall, Sprint stopped expanding its 4G WiMAX network and shifted to focus on LTE, effectively ending the standards battle - GSM and its successor 4G/LTE won the war.
LTE & 5G: Unified Global Standards
LTE became the global 4G standard, which nearly every phone manufacturer and cellular network embraced. And the same is true for 5G - but there are some important caveats.
Although all carriers use the same standardized technology, they still often use different and incompatible radio frequencies.
 First, even though LTE and 5G are global standards, the cellular frequency bands used around the world vary considerably. Each country controls how spectrum is used inside their borders, and different countries have approved different frequencies for cellular. So, even though everyone uses the same technical standard, a smartphone or cellular device isn't truly globally compatible unless it supports most cellular bands.
First, even though LTE and 5G are global standards, the cellular frequency bands used around the world vary considerably. Each country controls how spectrum is used inside their borders, and different countries have approved different frequencies for cellular. So, even though everyone uses the same technical standard, a smartphone or cellular device isn't truly globally compatible unless it supports most cellular bands.
 Secondly, the LTE standards are now complete—there is nothing more to add to LTE, as it's a fully mature technology. 5G standards, by contrast, are still evolving. A first generation 5G device will not support newer 5G standards that are in development. So until 5G is fully mature, with all standards published (not expected until around 2023), then you also need to account for which generation the modem in your device supports. Newer generations will have more capabilities than older generations.
Secondly, the LTE standards are now complete—there is nothing more to add to LTE, as it's a fully mature technology. 5G standards, by contrast, are still evolving. A first generation 5G device will not support newer 5G standards that are in development. So until 5G is fully mature, with all standards published (not expected until around 2023), then you also need to account for which generation the modem in your device supports. Newer generations will have more capabilities than older generations.
It's an LTE and 5G World
Even though the development of the LTE standards ended years ago, it will remain a relevant cellular technology for many years to come, so, like previous generational transitions, the move from 4G to 5G will not be quick, and there will be a long overlap period.
One different aspect of this transition is that 5G and LTE were designed to coexist from the start, making the transition much more seamless than the transition from 3G to 4G.
If you still use LTE-only devices, check out our 5G Resource Center for the latest developments and recommendations. However, 5G is now mainstream, and there are few reasons to avoid upgrading.
Network Retirements & Refarming For the Future
Cellular spectrum is a limited resource.
If you think of cellular spectrum like prime Las Vegas real estate, one of the side effects of technological advancement is easier to understand: Every so often, you have to blow up an old hotel to build a bigger and better one in the same place.
The same is true for cellular networks. As carriers move to embrace newer generations of technology, they need to eventually shut down older networks to free up the cellular spectrum for new, more efficient networks and technology.
This process is called "refarming" the network.
The downside of refarming is that devices based on older technologies will, over time, become slower, have less coverage, and eventually become useless when the old network is entirely shut down. If you have a 1G, 2G, or 3G device, it is now useless since those networks no longer exist.
But the upside is that newer technologies are faster and more efficient, making things (eventually) better for everyone. But that means you will eventually need to upgrade your devices and technology to keep online.
2G Shutdowns
T-Mobile is the only carrier in the United States that still utilizes a 2G network. It was originally announced that the T-Mobile 2G network would be shut down in January 2023, but it has continually been pushed back. The latest T-Mobile 2G shut-down date is tracked here and is slated for 2025.
T-Mobile's 2G has been able to continue even past 3G shutdowns because the remaining legacy 2G network uses only a few small slices of spectrum that aren't used for 3G, LTE, or 5G—and some legacy 2G systems, like wireless home alarms, have been slow to upgrade.
Verizon shut down its 2G network at the end of 2020, and AT&T shut down theirs in 2017. Sprint's 2G network was shut down in 2022 when T-Mobile shut down the Sprint 3G network after the two companies merged.
3G Shutdowns
All the major carriers have shut down their 3G networks, and older devices are left behind in the dustbin of technological history. 3G may still be found in some small local and regional providers and in some other countries, but even where 3G remains, it is transitioning to newer technology.
At this point, Verizon, AT&T, and T-Mobile have all forced 3G-only and incompatible 4G devices that still require a 3G connection off of their networks, and they refuse to activate any of these older devices.
Here is the history and a summary of each carrier's 3G shutdown, along with relevant links:
Verizon - December 31, 2022
- 3G was officially shut down on December 31, 2022.
- Here are Verizon's 3G/CDMA shutdown information and support articles:
AT&T - February 22nd, 2022
- 3G is officially gone as of February 22, 2022.
- Those considering the purchase of a used device or phone should ensure it is on one of AT&T's compatibility lists:
- Cricket (AT&T Prepaid Subsidiary) Shutdown information.
T-Mobile - July 1, 2022
- Official T-Mobile Network Evolution Page - T-Mobile officially shut down its 3G network on July 1st, 2022.
- Sprint
- Sprint's 3G CDMA network was retired on May 31, 2022.
- T-Mobile customers can check compatibility with T-Mobile's IMEI Check tool.
At this point, any devices from the pre-LTE era will not work on current networks.
Most 4G/LTE data-only devices weren't affected by the 3G shutdowns, but a few were because they utilize 3G for authentication. Some of these older 4G data devices required firmware updates to ensure compatibility.
On the other hand, many early 4G smartphones were impacted because they relied on 3G for voice calls. After the 3G network shutdown, only phones compatible with VoLTE (Voice Over LTE) are compatible—the carriers have kicked those devices off the network or forced users to upgrade.
Upcoming 4G Shutdowns
4G and LTE service will continue to be supported by Verizon, AT&T, and T-Mobile into the foreseeable future - probably until the end of this decade at least.
However, on June 30th, 2022, T-Mobile shut down the Sprint 4G/LTE network and is using that spectrum for the T-Mobile 5G network.
While it hasn't happened yet, carriers will begin refarming spectrum used for LTE into 5G in the next couple of years.
The Future of 5G Evolution To 6G
The 5G world is upon us, and it has evolved at a furious pace and continues to do so. We are now at the point where 5G is mainstream, and the current generation of 5G modems in cellular devices will have a long lifetime, even as technology and networks continue to evolve.
5G will continue to evolve for years to come, and most of the future standards are in active development. These improvements are codified in distinct 3GPP standards that the entire cellular industry follows.
Here's a quick summary of past, present, and future standards:
- Release 15 (5G Phase One) - The initial foundation for 5G compatibility.
- Release 16 (5G Phase Two) - Completes the foundation for long-term 5G capability.
- Release 17 (5G Phase Two Part one) - Support for low-power and low-cost "RedCap" devices. Support for "non-terrestrial networks," enabling 5G integration with different types of satellite-connected links.
- Release 18 (5G Advanced) - Many performance improvements, including expanded carrier aggregation and advanced MIMO techniques, and integration of AI technologies.
- Release 19 (5G Advanced Phase Two) - Continued enhancements and improvements from Rel. 18, including enhanced massive MIMO, AI, more robust satellite integration, more use cases, and better power efficiency.
- Release 20 (5G Advanced Phase Three) - Work started in March 2024 and likely won't be finalized until 2027. This standard is also intended to be the first to begin laying the groundwork for 6G.
- Release 21 - While not set in stone, this will likely be the first true 6G standard, with development starting around 2026-2027 and finalization around 2030.
The graphic below is from Qualcomm and illustrates the evolution from 5G to 5G Advanced to 6G via multiple releases of the 3GPP cellular standards. Note that the years on this chart reflect the periods the standards are under development - products implementing a given standard follow a year or two after a standard is finalized.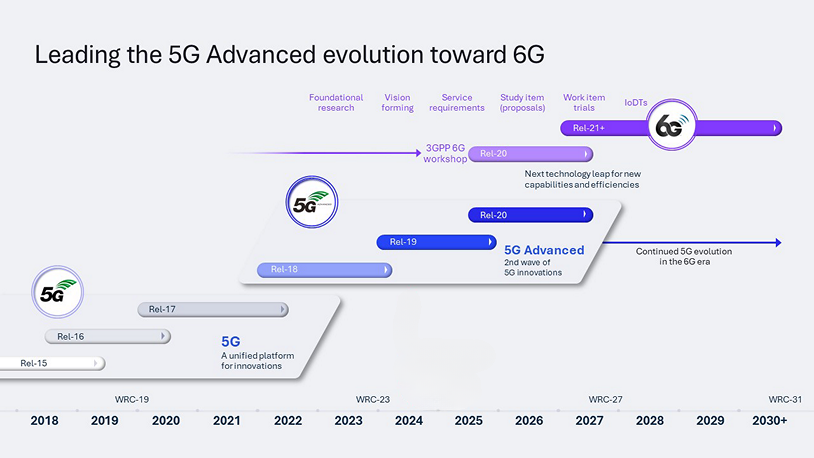
For more on 5G fundamentals, see our guide:
We also have a resource collection set up with all of our 5G news stories & guides that address different aspects of 5G:
6G - What to Expect?
The 6G cellular standard is being worked on, albeit in preliminary phases. Here are some of the highlighted goals that are being focused on:
- Support for many more frequency bands, including the upper mid-band range from 7-24 GHz and sub-terahertz frequencies (100-1000GHz) beyond mmWave.
- Massive speed improvements - potentially up to 1,000 Gbps (1 terabit per second) on the sub-terahertz frequencies. For consumer devices operating on lower frequencies, peak speeds will likely be far less than the theoretical potential - but still substantially faster than 5G speeds, which are expected to top out at around 20 Gbps.
- Additional native AI and Machine Learning integration for more intelligent network optimization and automation.
- Much greater latency and energy efficiency improvements.
- Seamless integration with satellite networks for true global coverage.
Reality Check: Speed And Capacity
Cellular companies love to brag about how fast their networks are.
But, once the connection is fast enough to stream HD video (around 5-10 Mbps), do most mobile users really need anything faster?
Faster and more responsive surfing is nice, but with data plan use restrictions (e.g., data caps, video throttling), there are very real downsides to speeding down the information highway too quickly.
Why, then, are carriers so gung-ho about ever-faster networks?
The key is capacity.
The faster the network can serve you whatever you’ve asked for, the faster it can move on to serving the next person.
With only so much spectrum to go around and networks in many areas already oversaturated, more speed is almost a matter of survival. This is why the carriers were so eager to shut down 3G networks quickly - slower 3G data networks hog up more network airtime compared to LTE and 5G, so it costs carriers more to serve 3G data than it would to send the same data to 4G/LTE or 5G users.
In short, newer technology allows carriers to provide faster service for more people and devices simultaneously using the same spectrum.
Capacity and speeds have already hit their peak with what LTE can provide. The transition to 5G will also provide more speed and capacity.
Summary: 5G Is Here But Still Evolving
Cellular technology is not fixed. It has been constantly evolving for over 40 years to accommodate increased demands on speed and capacity. As carriers evolve their networks, consumers must keep their cellular devices current to maximize access.
We are now in the middle of the 5G era, and 5G is mainstream. However, the carrier's LTE networks remain in place, so both LTE and 5G are supported. LTE will only decrease from here, especially once carriers aggressively move the spectrum to 5G.
To stay current, understand what you need to stay connected, and know when to upgrade, it's important to understand where we are currently at in the evolution and what's coming down the pike in the future.
Additional Reading
Related Guides:
- 5G Fundamentals
- Using Cellular Data for Mobile Internet Resources
- Understanding Cellular Modem Specifications
- Testing & Understanding Your Mobile Internet Speeds
- Understanding Cellular Frequencies
Related News Stories:
Explore the Resource Center
Have Questions?
Join our 'Library Desk':
Internet for RVers & Cruisers Facebook Group
We cross post news articles and guides, and can help point you in the right direction to our content here on the resource center.
It is with gratitude to our premium members that we're able to offer our free content - and for that, they also have access to our member Q&A areas for more in-depth guidance.
Become a Member
 The MIA is our premium membership - designed for those who consider mobile internet an important part of their lifestyle.
The MIA is our premium membership - designed for those who consider mobile internet an important part of their lifestyle.
In thanks for making content like this possible, we offer a bunch of additional perks. From interactive guidance, in-depth member exclusive content, discounts, alerts, classroom and ability to book private advising sessions.
Stay In the Know
We're constantly tracking the industry and analyzing new developments for mobile travelers. If you'd like to receive updates, we offer several ways:
- Subscribe to our free monthly newsletter
- Subscribe to our News Stories RSS Feed
- Subscribe to our YouTube Channel
- Follow our Facebook Page







 Mobile Internet Resource Center (dba Two Steps Beyond LLC) is founded by Chris & Cherie of
Mobile Internet Resource Center (dba Two Steps Beyond LLC) is founded by Chris & Cherie of